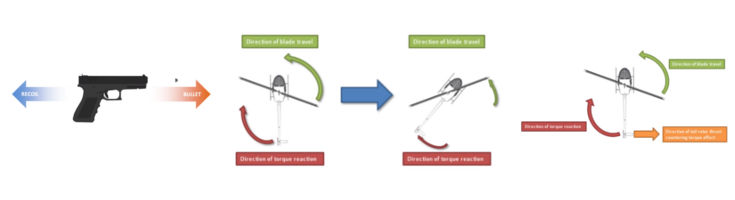
A basic rule of Newtonian physics is that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. So when you have the action of the rotation of the main rotor blades of a helicopter – the reaction will cause the body of the helicopter to move in the opposite direction. This torque reaction is offset by anti-torque systems like a tail rotor, Fenestron or NOTAR system. If the helicopter has more than one main rotor then they will counter-rotate to offset each other’s torque and remove the need for a tail rotor etc.
Video
The video below explains the helicopter torque reaction and the need for an anti-torque system:
Resources
- FAA Helicopter Flying Handbook Chapter 2 – Aerodynamics of Flight
- FAA Pilot’s Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge Chapter 5 – Aerodynamics of Flight
Related Videos
Airfoils
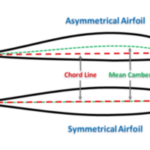
An airfoil is any surface that produces a useful aerodynamic force. Here are some examples of uses of those aerodynamic forces: Lift
Negative Lift
Stability
Thrust
Control
When talking about airfoils it is important to know the technical ...
Three Axes of Flight
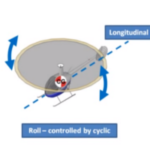
When maneuvering in the air, the helicopter moves around the Three Axes of Flight which all act through the helicopter's center of gravity (CG): Longitudinal Axis (Roll or Bank)
Lateral Axis (Pitch)
Vertical Axis (Yaw)
Video
The video below...